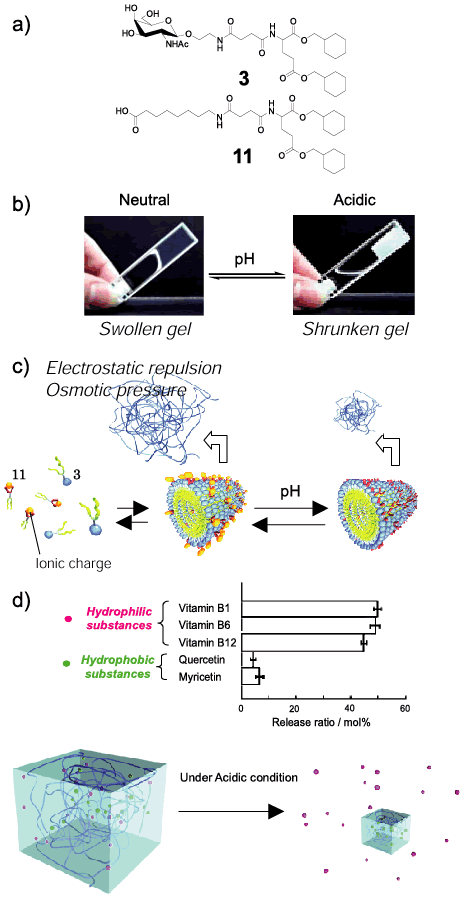

| Fig. 16 a) Chemical structures of a hydrogelator 3 and as an additional component, an amphiphilic carboxylic acid derivative 11 bearing the hydrophobic parts of 3. b) Photographs of a typical example of the pH‐responsive volume phase transition of the mixed hydrogel (equal quantities of 3 and 11) before and after shrinkage. c) Schematic illustration of the two-component gel strategy, and the subsequent pH-responsive volume change. d) The amount of five distinct substrates released after 60 min for vitamin B1, vitamin B6, vitamin B12 (hydrophilic substances), quercetin and myricetin (hydrophobic flavone derivatives). |